Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD) milling tools are high-performance cutting tools engineered for precision and durability. Unlike conventional carbide
or high-speed steel (HSS) tools, PCD milling tools use a layer of polycrystalline diamond bonded to a carbide substrate. This unique composition gives
them exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and longevity, making them ideal for challenging machining applications.

Material Composition: PCD milling tools consist of a dense layer of diamond particles fused into a solid mass and bonded to a tungsten carbide substrate. The diamond
layer's thickness varies depending on the tool's design and intended application.
Tool Geometry: PCD milling tools come in various geometries, including end mills, face mills, ball nose mills, and profile mills. The specific geometry
depends on the type of milling operation and material being machined.
Cutting Edges: PCD tools are renowned for their sharp cutting edges, which enable clean cuts and fine finishes. The precision in edge grinding
and shaping ensures a consistent performance.
Heat Resistance: While diamonds are less stable at high temperatures than other materials like cubic boron nitride (CBN), PCD milling tools still offer considerable heat resistance,
allowing high-speed operations with reduced risk of tool failure.
Durability: PCD tools are extremely durable, withstanding high rates of wear and tear over prolonged periods, making them ideal for high-volume production settings.
PCD milling tools are used in a range of industries, each requiring different applications and benefits.
Automotive Industry: PCD tools are widely used for milling aluminum engine components, transmission parts, and other automotive elements where high precision and long tool life
are crucial.
Aerospace Industry: In aerospace, these tools are used to machine lightweight materials like aluminum and carbon fiber composites, requiring precision and
minimal material waste.
Woodworking and Composites: PCD milling tools are ideal for cutting and shaping wood, particleboard, MDF, and composite materials due to their sharp edges and durability.
Electronics and Optics: In industries like electronics, where precision is critical, PCD tools are used to machine ceramics and other delicate materials with high
accuracy and surface quality.

The creation of PCD milling tools is a complex process involving multiple stages:
Sintering: The process begins with sintering diamond particles under high pressure and temperature, creating the polycrystalline diamond structure.
Bonding to Carbide Substrate: The diamond layer is bonded to a tungsten carbide substrate, providing structural support and enhancing durability.
Grinding and Shaping: The PCD tools are precision-ground to achieve the desired tool geometry and cutting edge quality. This process requires advanced equipment and skilled labor.
Quality Control: Each tool undergoes rigorous quality control to ensure it meets the required specifications and tolerances.
PCD milling tools offer several advantages over conventional tools:
Long Tool Life: The extreme hardness and wear resistance of polycrystalline diamond lead to a longer tool life compared to carbide or HSS tool
High-Quality Surface Finish: The sharp cutting edges enable fine surface finishes, reducing the need for additional finishing operations.
High-Speed Machining: PCD tools can operate at high speeds, increasing productivity and reducing machining time.
Cost-Efficiency: Although the initial cost is higher, the extended tool life and improved productivity make PCD tools cost-effective in high-volume production settings.
Versatility: PCD milling tools can be used for a wide range of materials, from aluminum and composites to ceramics and graphite
Drawing | Order code | R | l3 | d2 | l2 | l1 | Z Teeth |
| BMR015050660-1S | 1.5 | 5 | 6 | 40 | 60 | 1 |
BMR020060660-1S | 2 | 6 | 6 | 40 | 60 | 1 | |
BMR025070660-1S | 2.5 | 7 | 6 | 40 | 60 | 1 | |
BMR030080660-1S | 3 | 8 | 6 | 40 | 60 | 1 | |
BMR040100872-1S | 4 | 10 | 8 | 40 | 72 | 1 | |
BMR050121072-1S | 5 | 12 | 10 | 40 | 72 | 1 | |
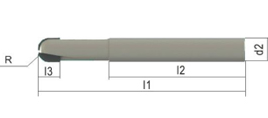 | BMR030080660-2S | 3 | 8 | 6 | 40 | 60 | 2 |
BMR040110872-2S | 4 | 11 | 8 | 40 | 72 | 2 | |
BMR050131097-2S | 5 | 13 | 10 | 50 | 97 | 2 | |
BMR060151297-2S | 6 | 15 | 12 | 50 | 97 | 2 | |
BMR070161497-2S | 7 | 16 | 14 | 50 | 97 | 2 | |
BMR080181697-2S | 8 | 18 | 16 | 50 | 97 | 2 | |
BMR090201897-2S | 9 | 20 | 18 | 50 | 97 | 2 | |
BMR100222097-2S | 10 | 22 | 20 | 50 | 97 | 2 |
Order code | d1 | l3 | d2 | l2 | l1 | Z Teeth | Drawing |
SM030560-1S | 3 | 5 | 4 | 40 | 60 | 1 |
|
SM040660-1S | 4 | 6 | 4 | 40 | 60 | 1 | |
SM050760-1S | 5 | 7 | 6 | 40 | 60 | 1 | |
SM060860-1S | 6 | 8 | 6 | 40 | 60 | 1 | |
SM081072-1S | 8 | 10 | 8 | 40 | 72 | 1 | |
SM101272-1S | 10 | 12 | 10 | 40 | 72 | 1 | |
DM060460-2S | 6 | 4 | 6 | 40 | 60 | 2 |
|
DM080472-2S | 8 | 4 | 8 | 40 | 72 | 2 | |
DM100572-2S | 10 | 5 | 10 | 40 | 72 | 2 | |
DM120697-2S | 12 | 6 | 12 | 50 | 97 | 2 | |
DM140797-2S | 14 | 7 | 14 | 50 | 97 | 2 | |
DM160897-2S | 16 | 8 | 16 | 50 | 97 | 2 | |
DM180997-2S | 18 | 9 | 18 | 50 | 97 | 2 | |
DM201097-2S | 20 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 97 | 2 |
To maximize the performance and longevity of PCD milling tools, consider the following best practices:
Appropriate Cooling and Lubrication: Use suitable cooling and lubrication methods to minimize heat buildup and prevent tool degradation.
Correct Speeds and Feeds: Follow the recommended machining parameters, including speeds and feeds, to ensure optimal performance and tool life.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Conduct regular inspections to detect signs of wear or damage. Proper maintenance can prolong tool life and ensure
consistent performance.
Proper Storage and Handling: PCD tools can be brittle, so careful handling and storage are essential to prevent chipping or breakage.
Application-Specific Tool Selection: Choose the appropriate PCD tool geometry and grade for the specific application and material being machined.
PCD milling tools are a highly valuable asset in the machining industry, offering exceptional hardness, durability, and precision. While they have a higher initial cost,
their long tool life and versatility can lead to significant cost savings and increased productivity in the long run. Understanding their characteristics, applications, and
best practices will help you get the most out of these advanced milling tools.
For all inquiries, please fill in the form below (* are required) to send us a brief message, and we will get back to you as soon as possible.